Explain the Different Types of Nutrient Cycles
The Phosphorus cycle is the movement of different forms of phosphorus through nature. Model 3 The Nitrogen Cycle.
Nutrient Cycling Crandall Park Trees
The producers of an ecosystem take up several basic inorganic.

. Some of the major biogeochemical cycles are as follows. It is one of the biogeochemical cycles in which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere geosphere hydrosphere atmosphere and pedosphere. The types of nutrient cycles largely fall under Sedimentary cycles- Reservoir in the sedimentary biogeo cycle is Earths crust and includes earth-bound elements such as phosphorus calcium iron and sulfur among others.
Some of it is hardened into layers and stored in the deep waters. Please list three different types of human activities that may affect nutrient cycles. Gaseous cycles- Reservoirs in the gaseous biogeo cycle are air or ocean and include carbon oxygen and nitrogen.
Animal eats sugar molecule. In the hydrologic cycle there occurs an interchange of compounds between the earths surface and the atmosphere via. 1 Water Cycle or Hydrologic Cycle 2 Carbon-Cycle 3 Nitrogen Cycle 4 Oxygen Cycle.
Here the chemical elements are always recycled whereas heat is dissipated. Denitrification by denitrifying baceria Further nitrification by nitrifying baceria Nitrification by nitrifying baceria Lightning. Sedimentary Nutrient Cycle 4.
Animal releases carbon dioxide into the air. 1 Water Cycle or Hydrologic Cycle 2 Carbon-Cycle 3 Nitrogen Cycle 4 Oxygen Cycle. It is essential for energy transfer.
The latter may include all the three major types of cycles ie hydrologic cycles gaseous nutrient cycles and. -found inside organisms living. They provide a source of nitrogen and phosphorus for cells.
The green plants when dead are buried into the soil that gets converted into fossil. These are the biogeochemical cycles in which the reservoir pool is generally lithosphere. There are two major types of biogeochemical cycles.
Trees and other plants take up mineral and non-mineral nutrients from the soil through their roots. Energy flow is a unidirectional and noncyclic pathway whereas the movement of mineral nutrients is cyclic. Nitrates and phosphates are two of these nutrients.
Mineral cycles include the carbon cycle sulfur cycle nitrogen cycle water cycle phosphorus cycle oxygen cycle among others that continually recycle along with other mineral nutrients into productive ecological nutrition. There are many other nutrient cycles that are important in ecology including a large number of trace mineral nutrient cycles. Give a bio molecule that contains these nutrients.
This water contains a lot of nutrients from the remains of dead organisms. Click again to see term. The producers of an ecosystem take up several basic inorganic nutrients from their non-living environment.
Tap again to see term. Carbon is thus stored in the plant. In forest environments the nutrient cycle involves animals plants fungi and bacteria living above- and below-ground the soil is alive as well as mineral components of soil dead leaves and wood and water from rain and snowfall.
These nutrients are stored in the leaves flowers and. Human activities are changing the rates of cycling of certain nutrients which may result in pollution and the depletion of natural resources. Upwelling is a process were water moves from deeper parts of the sea to the surface.
Tap card to see definition. Energy flows but the matter is always recycled. These are the biogeochemical cycles in which the reservoir pool is the atmosphere or hydrosphere.
These materials get transformed into the bio mass of the producers. Weathering and mining release the phosphorus in rocks into the terrestrial and marine ecosystems. N-fixing bacteria Found in root nodules of legumes Nitrogen fixation Nitrogen fixation Feeding.
Animal releases carbon dioxide into the air. Types of Biogeochemical Cycles. All green plants use carbon dioxide and sunlight for photosynthesis.
Nitrogen and phosphorus are plant essential nutrients that are currently in excess in many aquatic ecosystems due to runoff from urban and agricultural areas. Phosphorus is mostly available in solid matter. Hydrologic cycle or water cycle.
Nitrates in soil Atmospheric Nitrogen N. Biotic and abiotic components of ecosystems within which they exist as organic and inorganic compounds. There are three types of biogeochemical cycles.
Plant uses carbon dioxide to make sugar molecules. Nutrient Cycling in Aquatic Ecosystems. Hydrologic or water cycle.
Gascons Nutrient Cycle 3. To get a better idea see the movement of water which is a chemical compound H 2 O. Types of Nutrient Cycles.
Plant takes in carbon dioxide. -large complex molecules that all contain nitrogen. Based on the replacement period a nutrient cycle is referred to as Perfect or Imperfect cycle.
The movement of those elements and inorganic compounds that are essential to life can be conveniently designated as the nutrient cycling. What do nutrients cycle between. Please list three different types of human activities that may affect nutrient cycles.
Plant uses carbon dioxide to make sugar molecules. The following points highlight the top five types of biochemical cycle existing in ecosystem. This is how cycles are possible.
For example carbon cycle nitrogen cycle etc. This recycling of the nutrients through different components in an ecosystem is called the nutrient cycle or biogeochemical cycle. A perfect nutrient cycle is one in which nutrients are replaced as fast as they are.
Click card to see definition. Nutrient Cycling in Aquatic Ecosystems Active. Types of biogeochemical cycles.
Some of the major biogeochemical cycles are as follows.
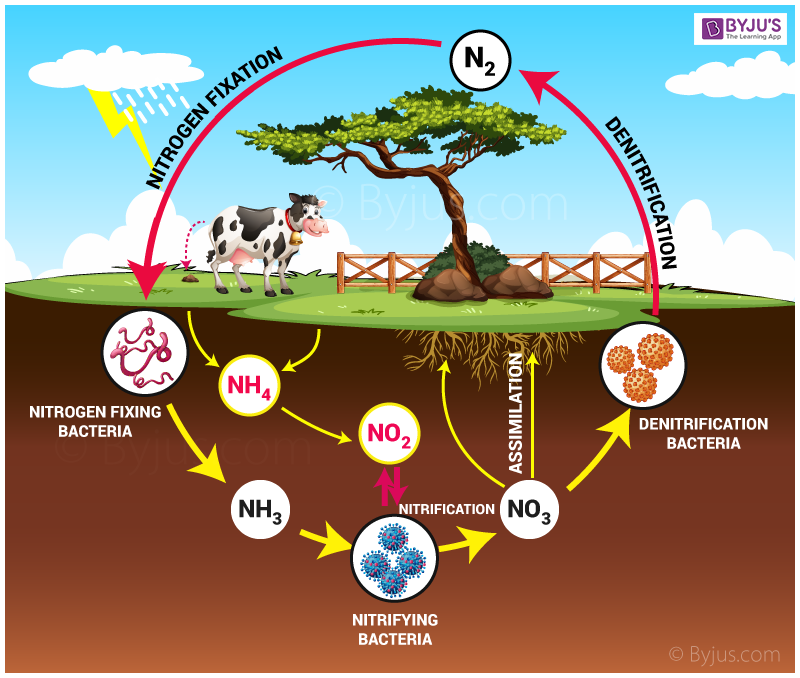
Nutrient Cycle Definition Examples And Importance
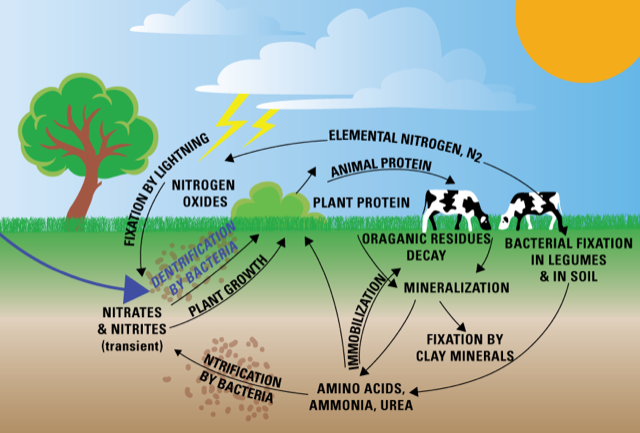
How Can We Restore Earth S Nutrient Cycles Greenpeace International
Nutrient Cycling Crandall Park Trees

What Is The Nutrient Cycle Definition Steps Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
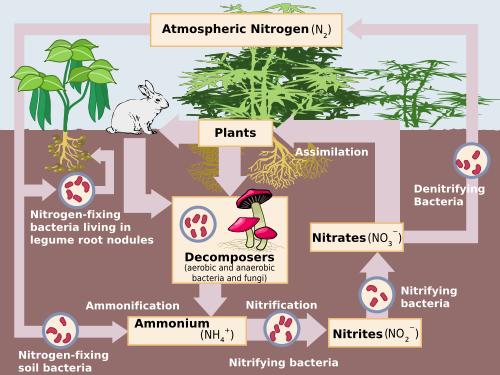
Science For Kids Nitrogen Cycle

A Conceptual Diagram Of Nutrient Cycling Of Forest Ecosystem Adapted Download Scientific Diagram
Nature S Nutrient Cycle European Environment Agency

Nitrogen Cycle Definition Steps Britannica

A Conceptual Diagram Of Nutrient Cycling Of Forest Ecosystem Adapted Download Scientific Diagram
What Is The Nutrient Cycle Definition Steps Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Biogeochemical Cycle Definition Examples With Questions And Videos

Nutrient Cycles Boundless Microbiology
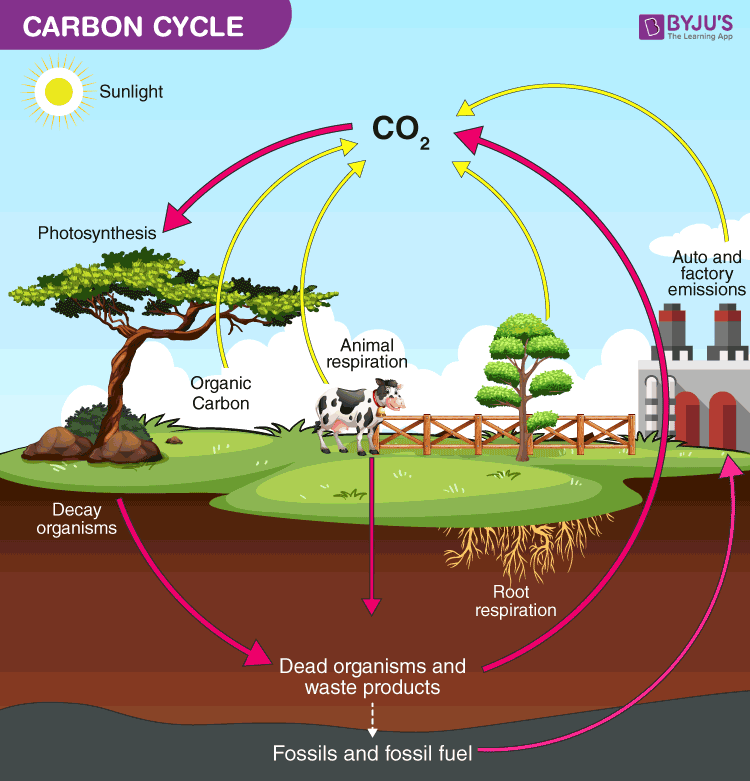
Nutrient Cycle Definition Examples And Importance
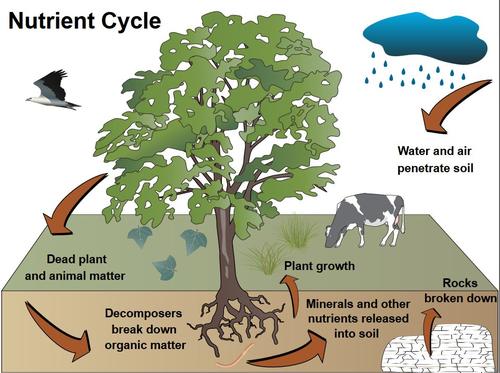
Nutrient Cycle Integrated Water Resource Management From Traditional Knowledge To Modern Techniques Department Of Earth Sciences

Nutrient Cycling Soil Carbon Cycle Ecosystem Stock Illustration 1719934036

Understanding The Nitrogen Cycle Beginners Education Algaebarn
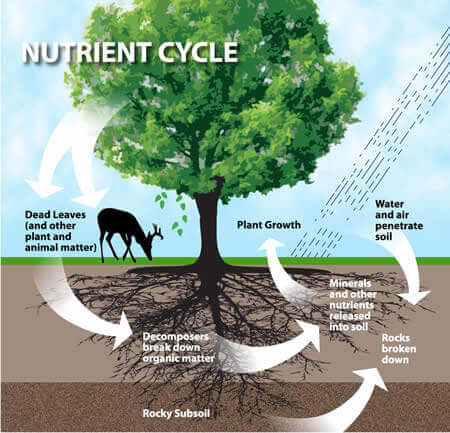
Carbon Cycle Nitrogen Cycle Phosphorus And Sulphur Cycle Pmf Ias
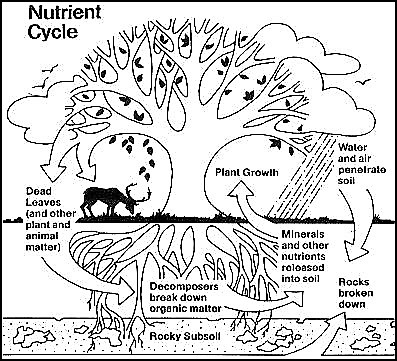
The Nutrient Cycle Sswm Find Tools For Sustainable Sanitation And Water Management
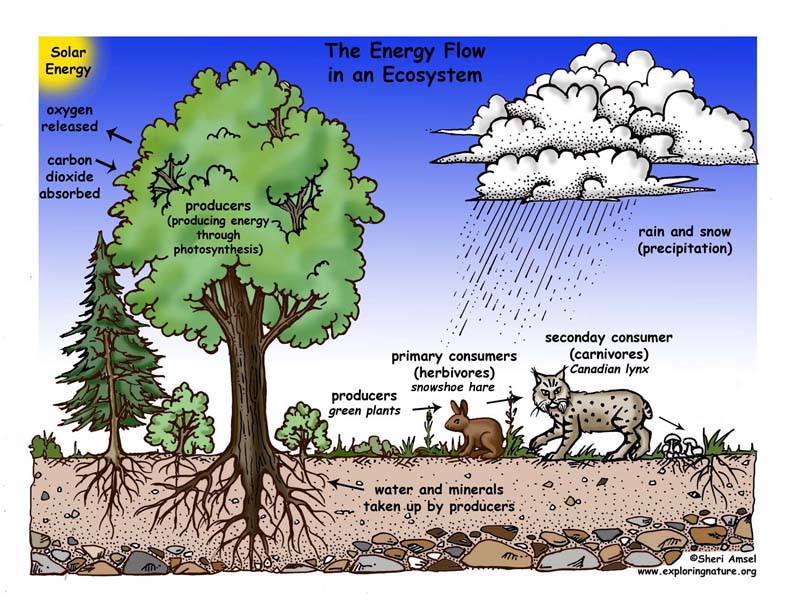
Comments
Post a Comment